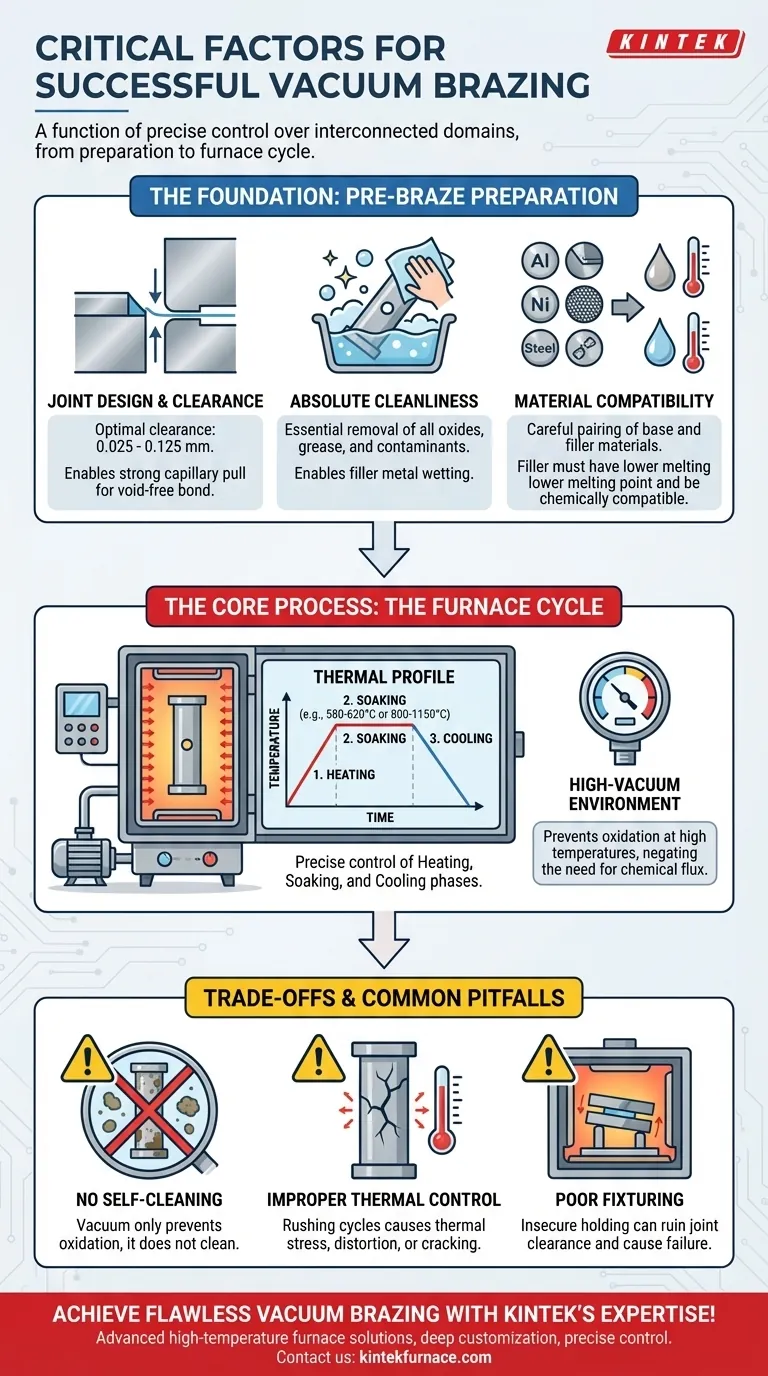
Successful vacuum brazing is a function of precise control over four interconnected domains. It requires an optimal joint design, meticulous pre-braze cleaning, the selection of compatible materials, and, most critically, the exact management of the thermal cycle within a high-vacuum environment to ensure a strong, clean, and distortion-free bond.
Vacuum brazing is not merely a heating process; it is the creation of a pristine environment where physics can do its work. Your success depends less on the final heating stage and more on the disciplined preparation of the components and the precise control of the entire furnace cycle.
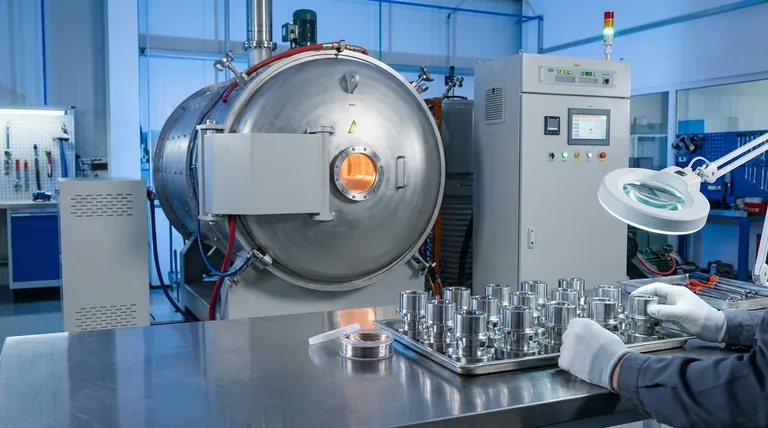

The Foundation: Pre-Braze Preparation
The quality of the final joint is determined long before the components enter the furnace. Flawless preparation is non-negotiable.
Mastering Joint Design and Clearance
The gap between the parts to be joined, known as the joint clearance, is the most critical design parameter. It dictates how the molten filler metal will be drawn into the joint.
A clearance of 0.025 mm to 0.125 mm is typically optimal. This narrow gap creates the capillary action necessary to pull the filler metal completely through the joint, ensuring a void-free bond.
Too large a gap weakens capillary force, leading to incomplete flow and a weak joint. Too small a gap can prevent the filler from entering at all.
Ensuring Absolute Cleanliness
The vacuum environment is preventative, not restorative. It stops new oxides from forming on heated metal but will not remove existing oxides, grease, or other contaminants.
Therefore, parts must be rigorously cleaned before assembly. This step ensures the molten filler metal can "wet" the surfaces of the base materials, which is essential for forming a strong metallurgical bond.
Assembly should occur in a clean environment to prevent recontamination before the parts are loaded into the furnace.
Selecting Compatible Materials
Successful brazing requires a careful pairing of the base materials (the parts being joined) and the filler metal (the brazing alloy).
The filler metal must have a melting point lower than the base materials. It must also be chemically compatible to promote wetting and flow without degrading the base materials during the thermal cycle.
The Core Process: The Furnace Cycle
Inside the furnace, a carefully orchestrated sequence of environmental and thermal changes transforms separate components into a single, integrated assembly.
Establishing the High-Vacuum Environment
The process begins by sealing the components inside the furnace chamber and using a vacuum pump to remove atmosphere, primarily oxygen.
This high-vacuum environment is the key advantage of the process. It eliminates the risk of oxidation at high temperatures, which would otherwise prevent a proper bond from forming and negates the need for chemical flux.
The Critical Role of the Thermal Profile
The furnace does not simply heat the parts. It executes a precise thermal profile with three distinct phases.
- Heating: A controlled, gradual ramp-up in temperature to prevent thermal shock and distortion.
- Soaking: Holding the assembly at the brazing temperature (e.g., 580-620°C for aluminum, 800-1150°C for other alloys) for a specific duration. This allows the temperature to equalize and the filler metal to melt completely.
- Cooling: A slow, controlled reduction in temperature to solidify the filler metal without inducing internal stresses or cracks.
How the Filler Metal Creates the Bond
At the designated brazing temperature, the filler metal melts. In the clean, oxide-free environment, it flows freely via capillary action into the precisely designed joint gap.
Upon cooling, the filler metal solidifies, creating a strong, permanent metallurgical bond between the components. The resulting joint is clean, bright, and requires no post-process cleaning.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Common Pitfalls
While powerful, vacuum brazing demands an understanding of its limitations to avoid costly failures.
The Myth of "Self-Cleaning"
A common mistake is assuming the vacuum will clean the parts. The vacuum only prevents oxidation; it does not remove pre-existing contamination. Dirty parts going into the furnace will always result in a failed braze.
The Risk of Improper Thermal Control
Rushing the heating or cooling cycles is a primary cause of failure. Rapid temperature changes induce thermal stress, leading to part distortion or cracking, especially when joining dissimilar materials with different expansion rates.
The Inefficiency of Poor Fixturing
Components must be held securely in the correct orientation throughout the furnace cycle. Poorly designed loading tools or fixtures can allow parts to shift during heating, ruining the joint clearance and causing the entire process to fail.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure success, align your focus with the most critical parameter for your specific outcome.
- If your primary focus is maximum joint strength and integrity: Prioritize meticulous pre-braze cleaning and maintaining precise joint clearance during assembly.
- If your primary focus is avoiding component distortion: Concentrate on designing a gradual, symmetrical heating and cooling cycle tailored to your materials.
- If your primary focus is process repeatability and scalability: Invest in high-quality, programmable vacuum furnaces and standardize your cleaning and assembly procedures.
By mastering these fundamental principles, you move from simply performing a process to engineering a perfect metallurgical bond.
Summary Table:
| Critical Factor | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Joint Design | Optimal clearance of 0.025-0.125 mm for capillary action |
| Pre-Braze Cleaning | Essential for removing contaminants to ensure wetting |
| Material Selection | Compatible base and filler metals with lower melting point |
| Thermal Profile | Controlled heating, soaking, and cooling to prevent stress |
| Vacuum Environment | High vacuum prevents oxidation without flux |
Achieve flawless vacuum brazing with KINTEK's expertise! We specialize in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, tailored for diverse laboratory needs. Leveraging our strong R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to meet your unique experimental requirements, ensuring precise thermal control and reliable results. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your brazing process and deliver superior bonds!
시각적 가이드
관련 제품
- 몰리브덴 진공 열처리로
- 2200 ℃ 텅스텐 진공 열처리 및 소결로
- 2200℃ 흑연 진공 열처리로
- 세라믹 섬유 라이너가 있는 진공 열처리로
- 진공 핫 프레스 용광로 기계 가열 진공 프레스 튜브 용광로



















